Spatial Ag Systems | 419-899-4490
Introduction
- Unfavorable weather during spring months can delay corn planting or make replanting necessary, if germination and emergence is poor.
- When corn planting is delayed, the growth and development of the crop is also delayed. This can make the crop more vulnerable to yield loss from diseases and insects since they can affect the crop at earlier stages of development relative to grain fill.
- Diligent scouting is especially important in late-planted corn to watch for potential issues and determine if a treatment is economically justified.
- This Crop Focus article provides a brief overview of select insects and diseases that can pose a greater risk to late planted corn.
Insects
Corn Rootworm
- Larvae feeding duration lasts from late May – late July.
- CRW larvae initially feed on root hairs and outer root tissue before burrowing deeper into the root.
- Corn often suffers physiological stress as a result of feeding, due to the hindrance of water and nutrient uptake.
- Late planted corn is at an increased risk of silk clipping due to presence of more rootworm beetles during pollination.
- Late planted fields have the potential to become a trap crop for egg laying when they are surrounded by earlier planted fields, increasing the risk of a high larva infestation the following year.

Figure 1. CRW larvae feeding on corn root. Photo courtesy of Jim Kalisch
Corn Earworm
- Warm and humid nights are favorable for CEW.
- Migrates north as conditions become suitable.
- Adults lay eggs on silks and larvae will feed down the ear.
- Larvae can be found in the whorl and foliage on younger plants.

Figure 2. CEW feeding in a straight line down the ear. Corn earworms are cannibalistic so there is typically only one found per infested ear.
European Corn Borer
- First generation ECB attacks corn starting in early June and can last until late July – early August.
- First generation larvae cause damage to the leaf surface and bore into the midrib before making their way to the stem.
- Second and third generations feed on the ear and also bore into the stalk.
- Yield loss potential from ECB damage varies by corn growth stage (Table 1).
- If no Bt traits are being utilized, first and second generation ECB can be controlled with insecticide with a scouting and integrated pest management program.
Table 1. Yield losses caused by ECB for various corn stages, based on physiological stresses and not stalk breakage or ear dropping (Krupke, Bledsoe, & Obermeyer, 2010).
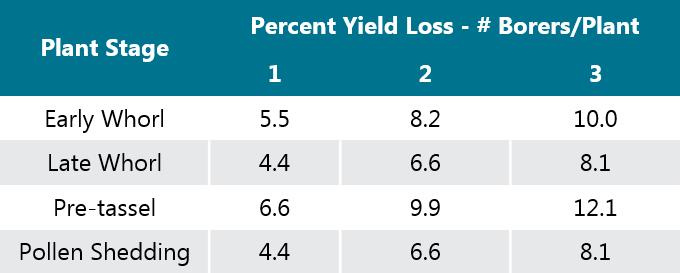

Figure 3. ECB larvae tunneled into corn stalk.
Fall Armyworm
- Late stage larvae can defoliate vegetative-stage corn, particularly in areas with grassy weeds.
- Fields with reduced tillage are at a higher risk than tilled ones.
- This pest is typically considered more of a southern pest when compared to the Corn Belt.

Figure 4. Fall armyworm feeding on vegetative tissue.
Diseases – Corn
Southern Rust
- Fungal disease caused by Puccinia polysora pathogen.
- Favored by high humidity and temperatures in the 80s and 90s.
- More frequent in the South, but may also spread into the Midwest by wind-blown spores, usually in late summer.
- Spreads very rapidly when conditions favor development. New infections may occur every seven days, epidemics may occur over large areas so fields may be damaged very quickly.

Figure 5. Corn leaf infected with southern rust. Note round to oval pustules, light brown to orange in color.
Northern Corn Leaf Blight
- Also known as the fungus Exserohilum turcicum, that overwinters in corn debris.
- Infection occurs when free water is present for 6-18 hours and temperatures are 65-80ºF (18-20ºC).
- Spores spread by rain splash or are carried on air currents.
- Infection can occur during any growth stage, but plants are most susceptible after pollination.
- Fungicides are available to manage this pathogen, if necessary.

Figure 6. NCLB lesions on corn leaf.

Figure 7. Close up of NCLB lesion.
Stalk Rots
- Depletion of nitrogen due to leaching makes stalks more prone to rotting.
- Specific rots are weather dependent.

Figure 8. Stalk depicting both anthracnose and Gibberella stalk rot.
Gray Leaf Spot
- Fungal disease caused by Cercospora zeae-maydis pathogen.
- GLS builds up in corn residue over time.
- Favored by warm temperatures and high humidity.
- Disease often spreads rapidly with favorable weather during late summer and early fall (during the grain fill period of corn development).
Southern Corn Leaf Blight
- Fungal disease caused by Cochliobolus heterostrophus (also known as Bipolaris maydis).
- Development is favored by warm (70 to 85ºF), moist weather and free water on the leaf.
- Thrives in warm-temperate or subtropical corn-growing environments, including the southeastern U.S.
- Spores are windblown or splashed by water to new crop leaves where they germinate and infect the plant.

Figure 9. GLS lesions (rectangular shape).

Figure 10. SCLB lesions (irregular shape).
Tar Spot
- Caused by the fungus Phyllachora maydis in the United States, can complex with Monographella maydis in Mexico.
- Dark fungal fruiting spots, associated with the name, can inhibit photosynthesis.
- Pathogen is favored by cool temperatures; 60-70ºF, or 16-20ºC; a high relative humidity, 75% or more, cloudy days, or 7+ hours of dew at night.
- Research is ongoing to determine the best management practices for this disease.

Figure 11. Tar spot of corn leaf. (Photo courtesy of Martin Chilvers.)
References
Krupke, C. H., Bledsoe, L. W., & Obermeyer, J. L. (2010). European Corn Borer in Field Corn. Purdue Extension.
Author: Madeline Henrickson, Pioneer Agronomy Sciences
June 2019
The foregoing is provided for informational use only. Please contact your Pioneer sales professional for information and suggestions specific to your operation. Product performance is variable and depends on many factors such as moisture and heat stress, soil type, management practices and environmental stress as well as disease and pest pressures. Individual results may vary. Pioneer® brand products are provided subject to the terms and conditions of purchase which are part of the labeling and purchase documents.